
Central Florida may be a hot spot for the ancient disease, perplexing analysts. They’re burrowing into the wonder.

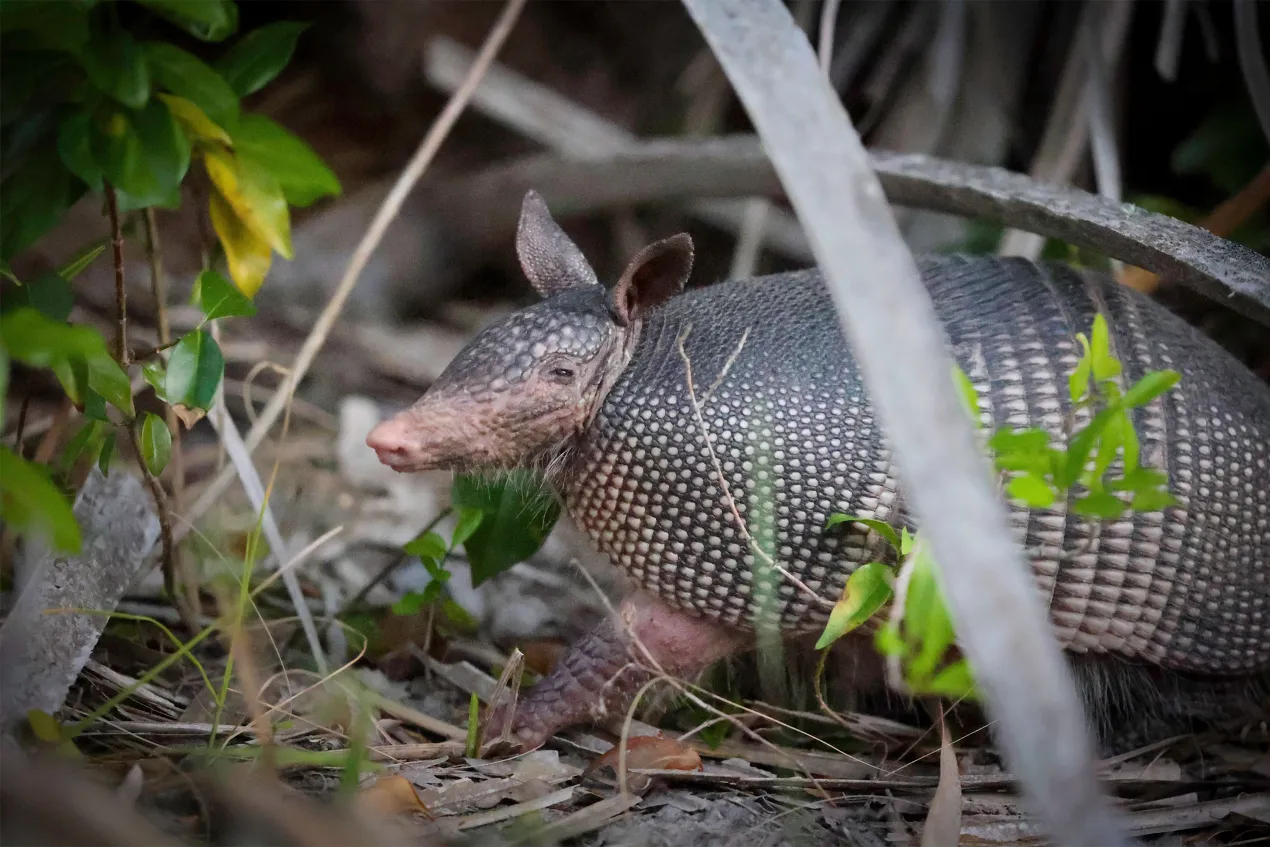
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — In an open-air barn at the edge of the College of Florida, veterinarian Juan Campos Krauer looks at a dead armadillo’s footpads and ears for signs of disease.
Its claws are twisted tight and secured in blood. Campos Krauer considers it was struck within the head whereas crossing a adjacent street.
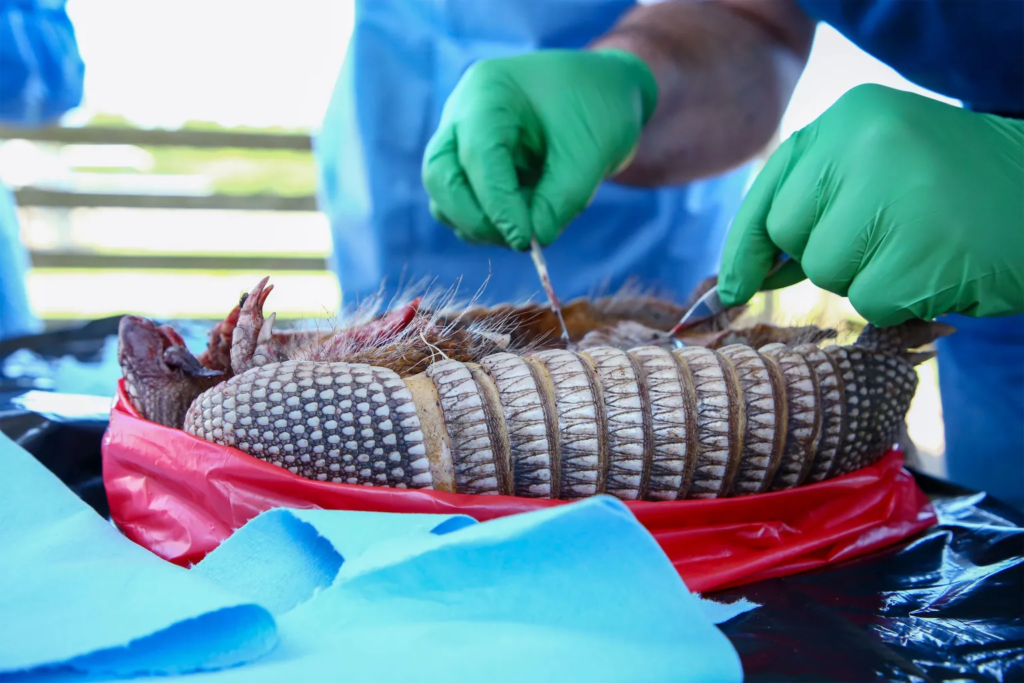
He at that point runs a surgical tool down its underside. He evacuates all the vital organs: heart, liver, kidneys. Once the examples are bottled up, they’re ordained for an ultra-cold cooler in his lab at the college.
Campos Krauer plans to test the armadillo for sickness, an old ailment moreover known as Hansen’s malady that can lead to nerve damage and distortion in people. He and other researchers are attempting to unravel a restorative puzzle: why Central Florida has ended up a hot spot for the age-old microscopic organisms that cause it.
Sickness remains uncommon within the Joined together States. But Florida, which frequently reports the foremost cases of any state, has seen an uptick in patients. The epicenter is east of Orlando. Brevard District detailed a stunning 13% of the nation’s 159 disease cases in 2020, agreeing to a Tampa Inlet Times examination of state and government information.
Numerous questions around the marvel stay unanswered. But disease specialists accept armadillos play a part in spreading the ailment to individuals. To superior get it who’s at risk and to anticipate contaminations, around 10 researchers joined up final year to examine. The gather incorporates analysts from the College of Florida, Colorado State College, and Emory College in Atlanta.
“How this transmission is happening, we truly do not know,” said Ramanuj Lahiri, chief of the research facility investigate department for the National Hansen’s Infection Program, which considers the microbes included and cares for disease patients over the nation.

‘Nothing Was Adding Up’
Disease is believed to be the most seasoned human disease in history. It likely has been sickening individuals for at slightest 100,000 a long time. The illness is highly stigmatized — within the Book of scriptures, it was depicted as a discipline for sin. In more cutting edge times, patients were separated in “colonies” around the world, counting in Hawaii and Louisiana.
In mild cases, the slow-growing microscopic organisms cause a number of injuries. In the event that cleared out untreated, they can paralyze the hands and feet.
But it’s really troublesome to drop sick with sickness, as the contamination isn’t exceptionally infectious. Anti-microbials can remedy the affliction in a year or two. They’re accessible for gratis through the government government and the World Wellbeing Organization, which propelled a campaign in the 1990s to dispense with sickness as a open wellbeing issue.
In 2000, detailed U.S. cases dropped to their most reduced point in decades with 77 diseases. But they afterward expanded, averaging around 180 per year from 2011 to 2020, concurring to information from the National Hansen’s Disease Program.
Amid that time, a inquisitive slant developed in Florida.
Within the to begin with decade of the 21st century, the state logged 67 cases. Miami-Dade District famous 20 contaminations — the foremost of any Florida district. The tremendous lion’s share of its cases were obtained exterior the U.S., concurring to a Times examination of Florida Office of Wellbeing information.

But over the another 10 a long time, recorded cases within the state more than doubled to 176 as Brevard District took center stage.
The district, whose populace is almost a fifth the measure of Miami-Dade’s, logged 85 contaminations amid that time — by distant the foremost of any province within the state and about half of all Florida cases. Within the past decade, Brevard famous just five cases.
Surprisingly, at slightest a quarter of Brevard’s contaminations were procured inside the state, not whereas the people were overseas. India, Brazil, and Indonesia analyze more disease cases than anyplace, detailing over 135,000 contaminations combined in 2022 alone. Individuals were getting debilitated indeed in spite of the fact that they hadn’t traveled to such regions or been in near contact with existing sickness patients, said Barry Inman, a previous disease transmission expert at the Brevard wellbeing division who explored the cases and resigned in 2021.
“Nothing was including up,” Inman said.
Many patients recalled touching armadillos, which are known to carry the microbes. But most didn’t, he said. Numerous went through a part of time outside, counting garden laborers and eager cultivators. The cases were as a rule gentle.
It was troublesome to nail down where people got the sickness, he included. Since the microscopic organisms grow so slowly, it can take anyplace from nine months to 20 a long time for indications to start.
Amoeba or Insect Culprits?
Heightened mindfulness of sickness could play a part in Brevard’s groundswell of cases.
Doctors must report disease to the wellbeing department. Yet Inman said numerous in the district didn’t know that, so he attempted to educate them after taking note cases within the late 2000s.
But that’s not the sole figure at play, Inman said.
“I do not think there’s any question in my intellect that something modern is going on,” he said.
Other parts of Central Florida have too recorded more contaminations. From 2011 to 2020, Polk Province logged 12 cases, tripling its numbers compared with the past 10 a long time. Volusia County noted 10 cases. It reported none the prior decade.
Researchers are sharpening in on armadillos. They suspect the burrowing critters may by implication cause infections through soil defilement.
Armadillos, which are ensured by difficult shells, serve as great has for the microbes, which do not like heat and can flourish within the animals whose body temperatures run from a cool 86-95 degrees.
Colonists likely brought the disease to the Modern World hundreds of a long time prior, and some way or another armadillos became infected, said Lahiri, the National Hansen’s Illness Program researcher. The nighttime warm blooded creatures can create lesions from the sickness fair as people can. More than 1 million armadillos involve Florida, evaluated Campos Krauer, an collaborator teacher within the College of Florida’s Office of Huge Creature Clinical Sciences.
How numerous carry leprosy is hazy. A ponder distributed in 2015 of more than 600 armadillos in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Mississippi found that approximately 16% appeared prove of disease. Open wellbeing specialists accept disease was already kept to armadillos west of the Mississippi Waterway, then spread east.
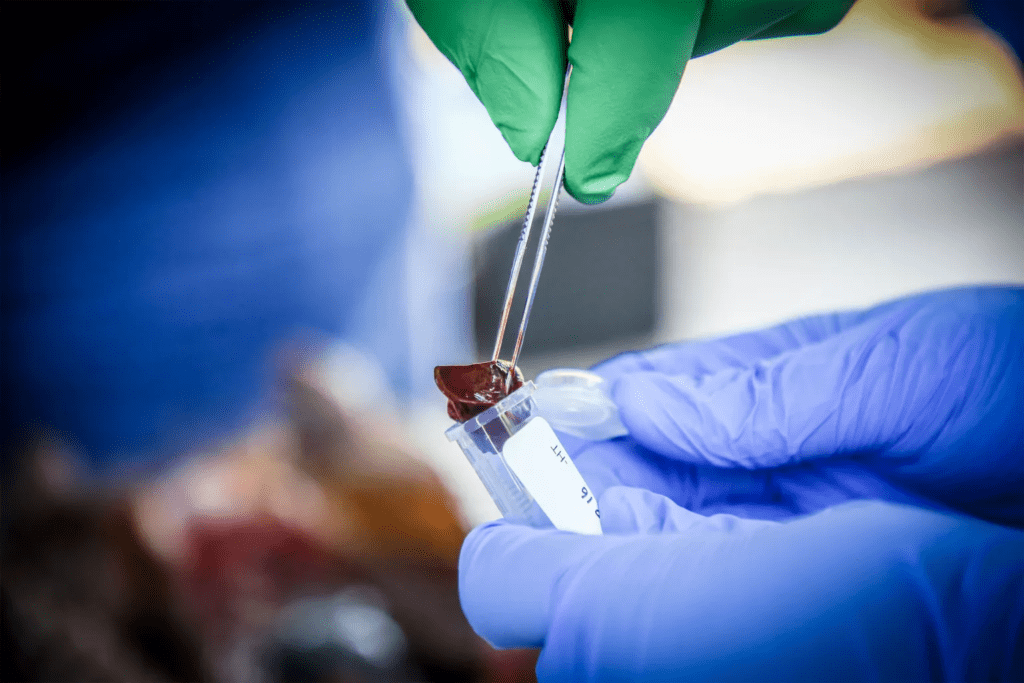
Dealing with the critters may be a known hazard. Lab inquire about shows that single-cell amoebas, which live in soil, can too carry the microscopic organisms.
Armadillos adore to burrow up and eat night crawlers, disappointing homeowners whose yards they harm. The creatures may shed the microscopic organisms whereas chasing for nourishment, passing it to amoebas, which seem afterward contaminate individuals.
Sickness specialists moreover wonder if insects help spread the disease. Blood-sucking ticks can be a culprit, lab investigate appears.
“Some people who are tainted have small to no introduction to the armadillo,” said Norman Beatty, an partner professor of medication at the College of Florida. “There is likely another source of transmission within the environment.”
Campos Krauer, who’s been searching Gainesville boulevards for armadillo roadkill, wants to accumulate contaminated creatures and let them break down in a fenced-off region, permitting the remains to drench into a plate of soil whereas flies lay eggs. He trusts to test the soil and hatchlings to see if they pick up the microscopic organisms.
Including to the interest could be a leprosy strain found only in Florida, agreeing to researchers.
Within the 2015 ponder, researchers discovered that seven armadillos from the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which is generally in Brevard but crosses into Volusia, carried a previously inconspicuous adaptation of the pathogen.
Ten patients within the locale were stricken with it, as well. At the hereditary level, the strain is comparable to another sort found in U.S. armadillos, said Charlotte Avanzi, a Colorado State University researcher who specializes in leprosy.
It’s unknown if the strain causes more serious malady, Lahiri said.
Reducing Risk
The public should not freeze around sickness, nor ought to individuals race to euthanize armadillos, researchers warn.
Researchers estimate that over 95% of the worldwide human population has a natural capacity to ward off the infection. They believe months of presentation to respiratory beads is needed for person-to-person transmission to occur.
But when diseases do happen, they can be destroying.
“If we way better get it it,” Campos Krauer said, “the way better ready to learn to live with it and reduce the risk.”
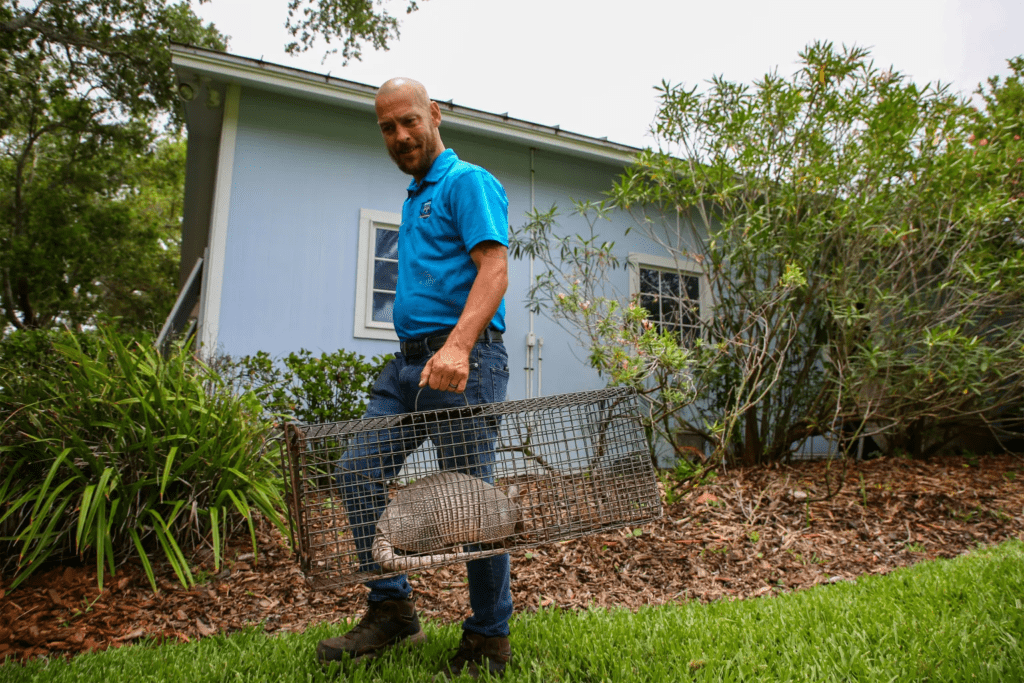

The modern inquire about may moreover give knowledge for other Southern states. Armadillos, which do not rest, have been moving north, Campos Krauer said, coming to ranges like Indiana and Virginia. They might go farther due to climate change.
People concerned approximately sickness can take simple precautions, restorative specialists say. Those working in earth ought to wear gloves and wash their hands a while later. Raising garden beds or encompassing them with a fence may restrain the chances of soil defilement. In the event that burrowing up an armadillo burrow, consider wearing a confront veil, Campos Krauer said.
Do not play with or eat the animals, added John Spencer, a researcher at Colorado State College who ponders disease transmission in Brazil. They’re lawful to hunt year-round in Florida without a license.
Campos Krauer’s group has so distant examined 16 dead armadillos found on Gainesville region roads, more than 100 miles from the state’s sickness epicenter, trying to induce a preparatory thought of how numerous carry the microbes.
None has tried positive however.

